- Phase 2 ALXN1210-NEPH-202 Study
- REDPINE: A Phase 3 Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel Group, Multicenter Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Remdesivir in Participants with Severely Reduced Kidney Function who are Hospitalized for COVID-19
- Mechanisms in Steroid-Responsive Airway Disease
- Role of Kruppel-Like Factors in Human Glomerular Disease
- Monitoring the progress of CKD 4-5 and ESRD patients
- Investigating the association of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) with chronic kidney disease (CKD) in World Trade Center (WTC) responders
- Blood endotoxin levels and kidney outcomes in ICU patients
- Human iPS cells for studying mechanisms of kidney disease
- Measurement of glucose absorption during peritoneal dialysis
- APOLLO Study
- Sensitivity and Specificity of screening markers for COVID-19 in patients with CKD
- National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) Clinical Characterization
- Therapeutic efficacy of Losartan for hypertension in COVID-19 patients
- Endotoxin Activity Assay Results and Kidney Outcomes in Intensive Care Unit
- Prevalence of Endotoxemia in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19
- Characterization of AKI with outcomes in patients with COVID-19
- Follow-up study of patients hospitalized with AKI and COVID-19 at Stony Brook University Hospital
- Industry Sponsored Clinical Research Studies: Polymyxin B cartridge hemoperfusion for patients with septic shock and COVID 19
- TIGRIS Trial: A Prospective, Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of PMX Cartridge in Addition to Standard Medical Care for Patients with Endotoxemic Septic Shock
- Association and Prognostic Significance of Pericardial Effusions in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease on Hemodialysis
- Biomarkers for cardiovascular disease progression in patients with chronic kidney diseas
Phase 2 ALXN1210-NEPH-202 Study
PI: Rula Abdulrahman
Primary Objective:
The purpose of this clinical trial is to evaluate the safety and efficacy (effectiveness against disease) of the study medication (ALXN1210 also known as ravulizumab or ULTOMIRIS ®) in participants with lupus nephritis (LN) or immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN), a rare chronic kidney disease.
REDPINE: A Phase 3 Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel Group, Multicenter Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Remdesivir in Participants with Severely Reduced Kidney Function who are Hospitalized for COVID-19
PI. Farrukh Koraishy
IRB# 2021-00318
Primary Objective:
To evaluate whether remdesivir (RDV, GS-5734™) reduces the composite risk of death or invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) through Day 29 in participants with severely reduced kidney function who are hospitalized for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Secondary Objectives:
- To evaluate whether RDV reduces the risk of death through Day 29
- To evaluate whether RDV reduces the risk of IMV through Day 29
- To evaluate the time to recovery (defined as satisfying category 1, 2, or 3 by the 8-point ordinal scale)
- To evaluate the effect of RDV on clinical status assessed by an 8-point ordinal scale at Day 15 and Day 29
- To evaluate the effect of RDV on renal replacement therapy (RRT)-free days (among those without end-stage kidney disease [ESKD]) through Day 29
- To evaluate the effect of RDV on recovery through Day 29
- To evaluate the safety and tolerability of RDV in participants with severely reduced kidney function who are hospitalized for COVID-19
The exploratory objectives of this study are as follows: - To evaluate the effect of RDV on days of hospitalization
- To evaluate peak serum creatinine (SCr) through Day 29
- To evaluate the effect of RDV on acute kidney injury (AKI; among those without ESKD) defined by:
o Stage 2 or 3 AKI through Day 29
o RRT-dependence (intermittent or continuous) through Day 29
11. To assess RDV impact on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) viral load
12. To identify and assess associations of biomarkers with disease progression and treatment response
13. To assess the pharmacokinetics (PK) of RDV, its metabolites, and sulfobutylether-beta-cyclodextrin (SBECD) in COVID-19 participants with severely reduced kidney function, including those on intermittent hemodialysis or continuous RRT
20. To evaluate the emergence of viral resistance to RDV
21. To evaluate mortality through Day 60
Mechanisms in Steroid-Responsive Airway Disease
PI: Dr. Sandeep Mallipattu
IRB# 2019-00347
The purpose of this project is to determine the factors mediating glucocorticoid-responsive airway disease. The specific aim is to identify clinical and genetic factors that might prognosticate glucocorticoid-responsive airway disease.
Role of Kruppel-Like Factors in Human Glomerular Disease
PI: Dr. Sandeep Mallipattu
IRB# 538128
The purpose of this project is to assess the role of Kruppel-Like Factors (KLFs) and related target genes in glomerular disease from previously completed kidney biopsy specimens at Stony Brook University Hospital (SBUH).
Monitoring the progress of CKD 4-5 and ESRD patients
Investigators: Dr. Sobia Khan, Dr. Rula Abdulrahman, Dr. Navdeep Kaur, Dr. Sandeep Mallipattu, Dr. Sheikh
IRB# 1756711-1
Investigating the association of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) with chronic kidney disease (CKD) in World Trade Center (WTC) responders
Extramural- R21 grant (Dept. of Health and Human Services and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
PI: Dr. Farrukh M. Koraishy
Blood endotoxin levels and kidney outcomes in ICU patients
Intramural- 2021/2022 Targeted Research Opportunity Program (Stony Brook University) – Clinical Research Awards
PI: Dr. Sian Piret
Co-PI: Dr. Sobia Khan
Human iPS cells for studying mechanisms of kidney disease
PI: Dr. Sandeep Mallipattu
IRB# 2021-00037
The purpose of this study is to build a biobank of induced pluripotent stem cell lines (iPSCs) from kidney disease patients treated by Stony Brook Medicine/Nephrology. A variety of urine-shed renal cell types will be used as starter cells for the purposes of reprogramming into the iPS cell state. A non-exhaustive list of experimental uses includes: growing patient specific organoids for toxicity and small molecule screens, determining polygenic molecular etiology underlying specific kidney disease states.
Measurement of glucose absorption during peritoneal dialysis
PI: Dr. Rula Abdulrahman
IRB# 2021-00247
Peritoneal dialysis is a way to remove waste products from patients with end stage renal disease. This method is becoming widely used and is recommended by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). Peritoneal Dialysis is performed by injecting a glucose-based solution in the peritoneal cavity for certain period of time, frequently during the days or the nights. The concerning issue with this modality is the amount of glucose absorption from the dialysis solution injected in the peritoneal cavity, and probably increasing the requirement of glucose lowering agents.
The goal of this study is to measure the actual amount of glucose absorbed by the patient during the dialysis treatment and comparing that value with the estimated glucose absorption that is usually calculated by certain available equations:
1. Grodstein formula: (11.3 xa-10.9) liters of dialysate, where xa is the average glucose concentration.
2. D/D0 formula: (1-D/D0)xi, where xi is the initial glucose instilled, using 4-hour D/D0 for continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) and dwell time D/D0 for automated peritoneal dialysis (APD).
The results of the data obtained will be used to achieve better glucose control for the patient, measuring the calories from that glucose being absorbed, and preventing the complications of metabolic abnormalities.
APOLLO Study
PI: Dr. Navdeep Kaur
The National Institutes of Health (NIH)-sponsored collaborative APOL1 Long-term Kidney Transplantation Outcomes Network (APOLLO) is charged with prospectively assessing the effects of renal-risk variants (RRVs) in the apolipoprotein L1 gene (APOL1) on outcomes for kidneys from donors with recent African ancestry and the recipients of their kidneys, after deceased- and living-donor renal transplantation. For the purposes of APOLLO, recent African ancestry is defined as individuals with similar genetic make-up to those currently residing in Africa. APOLLO will also study the impact of APOL1 RRVs on the health of living kidney donors with recent African ancestry.
Sensitivity and Specificity of screening markers for COVID-19 in patients with CKD
PI: Dr. Rula Abdulrahman
IRB# 2021-00092
The purpose of this project is to determine the sensitivity and specificity of screening for COVID19 in patients with chronic kidney disease,
Specific Aims:
-Determine the clinical symptoms and prescription medications associated with the development and severity of COVID19 in patients with chronic kidney disease.
QI Portion:
-Determine the compliance with vaccine against COVID-19.
National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) Clinical Characterization
Dr. Farrukh Koraishy
IRB# 2020-00604
The aim of this project is to clinically and geographically characterize adults (SA 1), children (SA 2) in the NIH-funded National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) database and their treatment pathways.
Therapeutic efficacy of Losartan for hypertension in COVID-19 patients
PI: Dr. Sandeep Mallipattu
IRB# 2020-00191
The purpose of this project is to conduct a pilot study on the therapeutic efficacy and safety of losartan in the treatment of hypertension in COVID-19 positive patients.
1. Primary Aim: Determine the therapeutic efficacy and safety of losartan in the management of hypertension in COVID-19 positive patients.
2. Secondary Aim: Determine whether treatment with losartan for hypertension in COVID-19 positive patients improves overall clinical outcomes.
Endotoxin Activity Assay Results and Kidney Outcomes in Intensive Care Unit
PI: Dr. Sobia Khan
IRB# 2020-00592
We would like to investigate the relationship between Endotoxin Activity Assay (EAA) results and health outcomes of diverse cohort of patients admitted to the intensive care unit in Stony Brook University Hospital in 2020. This is a prospective study in which the EAA results will be analyzed over time.
Prevalence of Endotoxemia in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19
PI: Dr. Sobia Khan
IRB# 2020-00474
This was a retrospective study to investigate whether the Endotoxin Activity Assay level prognosticates acute kidney injury. We also investigated if the prevalence of increased endotoxemia coincided with increased hospital stay.
Characterization of AKI with outcomes in patients with COVID-19
PI: Dr. Farrukh Koraishy
IRB# 2020-00239
The purpose of this project is to characterize acute kidney injury (AKI) COVID-19 patients and to determine the association of chronic kidney disease (CKD)/end-stage renal disease (ESRD), hypertension (HTN), intravenous fluids (IVFs) & angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs)/angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) with outcomes (AKI, mechanical ventilation and death in COVID-19 patients
Specific Aims:
1. Determine the type of AKI and its associated risk factors in patients with COVID-19 disease.
2. Determine the association of CKD/ESRD with AKI, ARDS and death in patients with COVID-19 disease.
3. Determine the association of HTN with AKI, ARDS and death in patients with COVID-19 disease.
4. Determine the association of ACEI/ARBs with AKI, ARDS and death in patients with COVID-19 disease.
5. Determine the association of IVFs with AKI, ARDS and death in patients with COVID-19 disease.
Follow-up study of patients hospitalized with AKI and COVID-19 at Stony Brook University Hospital
PI: Dr. Farrukh Koraishy
IRB# 2020-00461
This is an observational prospective study to determine the post-discharge outcomes of patients admitted at Stony Brook Hospital for acute kidney injury (AKI) and COVID-19 between March 2020 and May 2020.
Industry Sponsored Clinical Research Studies:
Polymyxin B cartridge hemoperfusion for patients with septic shock and COVID 19
PI: Dr. Sandeep Mallipattu
IRB# 2020-00267
The PMX cartridge will be utilized to treat critically ill patients with septic shock who also have the COVID 19 virus. The objective will be to observe the efficacy of the PMX cartridge with a focus on safety of use in this population. Overall design: Prospective, interventional, clinical investigation of PMX cartridge use.
Study Objectives:
1. To observe the 28 day mortality rate for patients with COVID 19 who are treated with the PMX cartridge.
2. To observe for adverse events related to the use of the PMX cartridge, associated heparin use (if any) and of the venous access line if placed only for the purpose of this protocol.
TIGRIS Trial: A Prospective, Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of PMX Cartridge in Addition to Standard Medical Care for Patients with Endotoxemic Septic Shock
PI: Dr. Sobia Khan
IRB# 2020-00475
Primary Objectives:
The primary objective is to compare the safety and efficacy of the PMX cartridge (Toraymyxin) based on mortality at 28 days in patients with septic shock and endotoxemia who are treated with standard medical care plus the use of the PMX cartridge, versus patients who receive standard medical care alone.
Secondary Objectives:
1. To compare changes in mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) from Day 0 to Day 3 in each group.
2. To compare changes in vasopressor doses from Day 0 to Day 3 in each group.
3. To compare the survival time from baseline to death within 28 days in each group.
4. To compare mortality at 28 days post baseline for patients with baseline norepinephrine dose. >0.1 mcg/kg/min in each group.
5. To compare mortality at 14 days post baseline in each group.
6. To compare total duration of vasopressor use from Day 0 to Day 3 in each group.
Association and Prognostic Significance of Pericardial Effusions in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease on Hemodialysis
PI: Dr. Sandeep Mallipattu
IRB# 1144488
The goals of this study are to investigate the prevalence and prognostic implications, including symptomatic pericardial disease and early mortality, of pericardial effusions, as measured by echocardiography, in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) on hemodialysis.
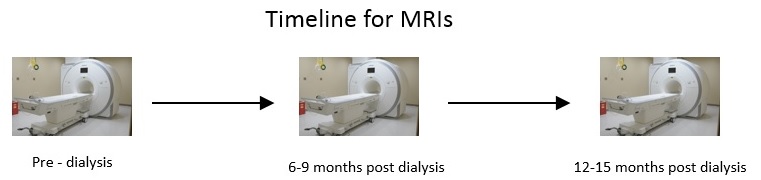
Biomarkers for cardiovascular disease progression in patients with chronic kidney disease
PI: Dr. Leonard Arbeit
IRB# 1013556
The goals of this study are to investigate the rate of progression of cardiac fibrosis, diastolic dysfunction, and vascular stiffness in patients from pre-dialysis to 1 year after initiation of dialysis, as well as to identify key biomarkers that may be able to predict the development and progression of cardiac fibrosis and eventual heart failure.
Patients are recruited from Dialysis Clinic Inc. and Stony Brook Nephrology Outpatient clinic at 26 Research Way. Patients must have CKD Stage 5 and/or approaching dialysis to be eligible for the study. Each study participant visits St. Francis Hospital for a cardiac MRI 3 times over the course of a year. Blood is collected around the time of each MRI to investigate for potential biomarkers. Clinical data such as blood pressure, hematocrit, myocardial mass, ejection fraction, and more are recorded for each patient at each MRI visit. This enables the researchers to track the progress of the patient over the year.
Kidney Biopsy Biobank
PI: Dr. Sandeep Mallipattu
IRB# 798611
The Biobank is a research collaboration between Stony Brook Nephrology and Pathology Departments.
Each patient undergoing a biopsy (native or transplant) procedure is eligible for the study. Patients are consented prior to their procedure and blood and urine samples are collected. Remaining samples of the biopsy (post-procedure) that are not used for diagnostic purposes are stored in the biobank. There are over 500 specimens collected since 2014.
Mechanisms in the progression of diabetic kidney disease
PI: Dr. Sandeep Mallipattu
IRB# 1088013
The goal is to identify key molecules in serum and urine that might cause the development and progression of diabetic kidney disease.
Patients with Diabetes (Type 1 & 2) were recruited at Stony Brook Endocrinology Outpatient Clinic at 26 Research Way and blood and urine samples were collected to identify markers that might predict the progression and/or development of diabetic kidney disease using cell-based functional assays and proteomics.
1. Therapeutic efficacy of Losartan for hypertension in COVID-19 patients
PI: Dr. Sandeep Mallipattu
IRB# 2020-00191
2. Prevalence of Endotoxemia in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19
PI: Dr. Sobia Khan
IRB# 2020-00474
3. Polymyxin B cartridge hemoperfusion for patients with septic shock and COVID 19
PI: Dr. Sandeep Mallipattu
IRB# 2020-00267

